Institutt for klinisk medisin: Recent submissions
Now showing items 1101-1120 of 1800
-
C-reactive protein and risk of venous thromboembolism: Results from a population-based case-crossover study
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-04-19)Long-term, low-grade inflammation does not seem to be a risk factor for venous thromboembolism. The impact of acute inflammation, regardless of cause, on risk of venous thromboembolism is scarcely studied. We aimed to investigate the impact of acute inflammation, assessed by C-reactive protein, on short-term risk of venous thromboembolism. We conducted a case-crossover study of patients with venous ... -
Social media for health promotion in diabetes: study protocol for a participatory public health intervention design
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-06-05)BACKGROUND: Participatory health approaches are increasingly drawing attention among the scientific community, and could be used for health promotion programmes on diabetes through social media. The main aim of this project is to research how to best use social media to promote healthy lifestyles with and within the Norwegian population. <br> <br> METHODS: The design of the health promotion ... -
Analysing mHealth usage logs in RCTs: Explaining participants’ interactions with type 2 diabetes self-management tools
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-08-30)<p><i>Background</i>: The Introduction of mobile health (mHealth) devices to health intervention studies challenges us as researchers to adapt how we analyse the impact of these technologies. For interventions involving chronic illness self-management, we must consider changes in behaviour in addition to changes in health. Fortunately, these mHealth technologies can record participants’ interactions ... -
Staphylococcus aureus Membrane-derived Vesicles Promote Bacterial Virulence and Confer Protective Immunity in Murine Infection Models
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-02-20)<i>Staphylococcus aureus</i> produces membrane-derived vesicles (MVs), which share functional properties to outer membrane vesicles. Atomic force microscopy revealed that <i>S. aureus</i>-derived MVs are associated with the bacterial surface or released into the surrounding environment depending on bacterial growth conditions. By using a comparative proteomic approach, a total of 131 and 617 proteins ... -
Social media use in interventions for diabetes: Rapid evidence-based review
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-08-10)<p><i>BACKGROUND</i>: Health authorities recommend educating diabetic patients and their families and initiating measures aimed at improving self-management, promoting a positive behavior change, and reducing the risk of complications. Social media could provide valid channel to intervene in and deliver diabetes education. However, it is not well known whether the use of these channels in such ... -
A comparison of CT based measures of skeletal muscle mass and density from the Th4 and L3 levels in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-09-25)Background:<br> Muscle mass and density assessed from CT-images at the L3 level are prognostic for survival and predict toxicity in cancer patients. However, L3 is not always included on routine CT-scans. We aimed to investigate whether images at the Th4 level may be used instead. <br> Methods:<br> Patients from three chemotherapy trials in advanced NSCLC were eligible (n = 1305). Skeletal muscle ... -
Osteoprotegerin is associated with major bleeding but not with cardiovascular outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes: Insights from the PLATO (Platelet Inhibition and Patient Outcomes) trial
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-01-12)Background: <br>Elevated levels of osteoprotegerin, a secreted tumor necrosis factor–related molecule, might be associated with adverse outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease. We measured plasma osteoprotegerin concentrations on hospital admission, at discharge, and at 1 and 6 months after discharge in a predefined subset (n=5135) of patients with acute coronary syndromes in the PLATO ... -
Genome-Wide DNA Methylation in Treatment-Naïve Ulcerative Colitis
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-08-22)<p><i>Background and Aims</i>: The aim of this study was to investigate the genome-wide DNA methylation status in treatment-naïve ulcerative colitis [UC], and to explore the relationship between DNA methylation patterns and gene expression levels in tissue biopsies from a well-stratified treatment-naïve UC patient group.</p> <p><i>Methods</i>; Mucosal biopsies from treatment-naïve patients [n = ... -
Non-linear optical microscopy as a novel quantitative and label-free imaging modality to improve the assessment of tissue-engineered cartilage
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2017-10)Objective: <br>Current systems to evaluate outcomes from tissue-engineered cartilage (TEC) are sub-optimal. The main purpose of our study was to demonstrate the use of second harmonic generation (SHG) microscopy as a novel quantitative approach to assess collagen deposition in laboratory made cartilage constructs. <br>Methods: <br>Scaffold-free cartilage constructs were obtained by condensation ... -
Violence and child mental health in Brazil: The Itaboraí Youth Study methods and findings
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-01-17)<p><i>Objectives</i>: To demonstrate a study design that could be useful in low‐resource and violent urban settings and to estimate the prevalence of child violence exposure (at home, community, and school) and child mental health problems in a low‐income medium‐size city.</p> <p><i>Methods</i>: The Itaboraí Youth Study is a Norway–Brazil collaborative longitudinal study conducted in Itaboraí ... -
Survival in Limited Disease Small Cell Lung Cancer According to N3 Lymph Node Involvement
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-02)Background/Aim: <br>There are several definitions of limited disease (LD) in small cell lung cancer (SCLC), differing with respect to N3 disease accepted. We analyzed patients from a randomized trial comparing two schedules of thoracic radiotherapy (TRT) in LD SCLC to investigate whether there were survival differences between N3 subcategories (n=144). Patients and <br>Methods: <br>Patients ... -
Routine deferred computed tomography for patients with suspected urolithiasis is low-value healthcare
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2016-11-23)<p><i>Objective - </i>The aim of this study was to investigate the benefits of deferred routine computed tomography of the kidneys, ureters and bladder (CT KUB) for patients with a self-limiting episode of suspected urolithiasis. <p><i>Materials and methods - </i>The study comprised a case series of consecutive patients examined with deferred routine CT KUB for control of suspected urolithiasis. ... -
Kurativ kateterbehandling av atrieflimmer
(Research report; Forskningsrapport, 2006)Atrieflimmer er den hyppigst forekommende hjerterytmeforstyrrelse av klinisk betydning, og berører ca 45 000 pasienter i Norge. Medikamentell behandling gir tilfredsstillende effekt hos flertallet, men man må se etter alternativer for de som ikke tåler eller responderer på medikamenter. For disse kan kateterbehandling med bruk av for eksempel radiofrekvensablasjon være en mulighet. Radiofrekvensablasjon ... -
Gas embolism during surgery. A complement mediated condition?
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2017-10-01)<p><i>Introduction</i>: Venous air embolism (VAE) may arise during surgical procedures. VAE might be complicated with a systemic inflammatory response, disseminated intervascular coagulation, multi-organ failure and cardiovascular collapse. During a short time-span, three patients at our institution developed signs of VAE in conjunction with gynecological surgery. One died, one developed severe ... -
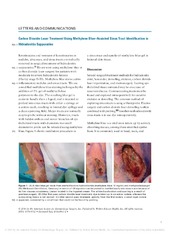
Carbon Dioxide Laser Treatment Using Methylene Blue–Assisted Sinus Tract Identification in Hidradenitis Suppurativa
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2016-11)Keratinocytes and remnant of keratinocytes in nodules, abscesses, and sinus tracts are radically removed in surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa.1 We are now using methylene blue in carbon dioxide laser surgery for patients with moderate to severe hidradenitis lesions (Hurley stage II-III). Methylene blue stains active inflammatory nodules and sinus tracts. We use a modified methylene blue ... -
An evaluation by the Norwegian Health Care Supervision Authorities of events involving death or injuries in maternity care
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-06-15)<p><i>Introduction</i>: We aimed to determine how serious adverse events in obstetrics were assessed by supervision authorities.</p> <p><i>Material and methods</i>: We selected cases investigated by supervision authorities during 2009‐2013. We analyzed information about who reported the event, the outcomes of the mother and infant, and whether events resulted from errors at the individual or ... -
How clinicians make decisions about CTOs in ACT: a qualitative study
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-09-22)<p><i>Background</i> - The first 12 Norwegian assertive community treatment (ACT) teams were piloted from 2009 to 2011. Of the 338 patients included during the teams’ first year of operation, 38% were subject to community treatment orders (CTOs). In Norway as in many other Western countries, the use of CTOs is relatively high despite lack of robust evidence for their effectiveness. The purpose of ... -
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF‑β)in adolescent chronic fatigue syndrome
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2017-12-04)<i>Background</i>: Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is a prevalent and disabling condition among adolescent. The disease mechanisms are unknown. Previous studies have suggested elevated plasma levels of several cytokines, but a recent meta-analysis of 38 articles found that of 77 diferent cytokines measured in plasma, transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) was the only one that was elevated in patients ... -
Combined Inhibition of C5 and CD14 Attenuates Systemic Inflammation in a Piglet Model of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
(Journal article; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed, 2018-02-27)<p><i>Background</i>: Meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS) is a severe lung condition affecting newborns and it can lead to a systemic inflammatory response. We previously documented complement activation and cytokine release in a piglet MAS model. Additionally, we showed ex vivo that meconium-induced inflammation was dependent on complement and Toll-like receptors.</p> <p><i>Objectives</i>: To ... -
Bypassing adverse injection reactions to nanoparticles through shape modification and attachment to erythrocytes
(Journal article; Manuskript; Tidsskriftartikkel; Peer reviewed; Preprint, 2017-04-10)Intravenously injected nanopharmaceuticals, including PEGylated nanoparticles, induce adverse cardiopulmonary reactions in sensitive human subjects, and these reactions are highly reproducible in pigs. Although the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood, roles for both the complement system and reactive macrophages have been implicated. Here, we show the dominance and importance of robust ...


 English
English norsk
norsk